Major Genes that could affect Hair Thickness
More than 200 genes have been identified as genetic factors that can affect hair loss.
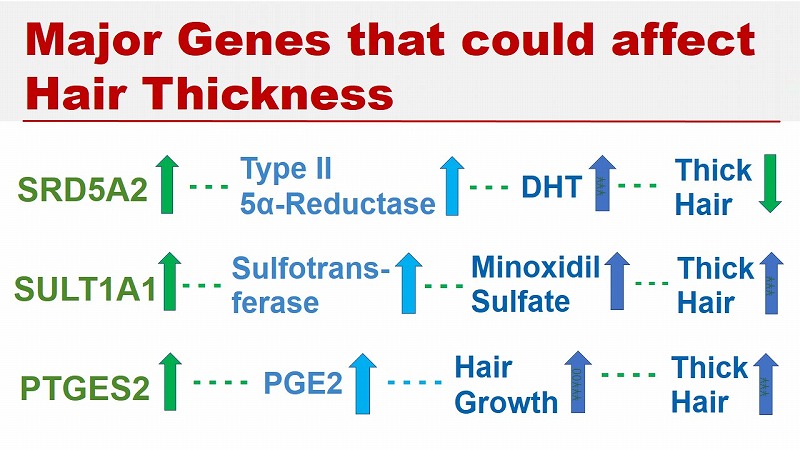
The three most important of them include SRD5A2, SULT1A1 and PTGES2.
SRD5A2 is a gene encoding the human 5α-reductase type II enzyme.
Higher activity of the 5α-reductase type II enzyme results in higher DHT levels, which leads to progression of hair loss due to AGA.
SULT1A1 gene is associated with the enzymatic activity of sulfotransferase, which converts minoxidil to its active form of minoxidil sulfate. An increase in the level of minoxidil sulfate results in an increase in hair thickness and density.
The low enzyme activity of sulfotransferase leads to a decrease in responsiveness to minoxidil, which can be found in about 20% of the population.
PTGES2 gene is involved in the activity of the PTGES2 enzyme. Fibroblasts produce PGE2, which increases hair thickness.
PTGES2 gene encodes the synthesis of PGE2, which induces hair growth.
Gene Analysis:
SRD5A2, SULT1A1 and PTGES2 Genes
Analysis of the SRD5A2, SULT1A1, and PTGES2 genes is already underway. The author would say that the results of the analysis would give us information about the genetic predisposition regarding individual responsiveness to hair growth treatment with 5α-reductase inhibitors and minoxidil.
Analysis of these three genes can tell whether a patient is a responder or a non-responder to finasteride, dutasteride and minoxidil.
With this information, people may be able to choose the most effective hair restoration medicine for each patient before hair loss treatment.
In the near future, genetic analysis may make it possible to treat hair loss individually.
Basic Research on Androgenetic Alopecia (Vol.3)
Gene Analysis and Other Issues, Summary

The latest information on genetic research about AGA has been discussed in this chapter.
Understanding the mechanism of AGA will give us important information about the therapeutic and preventive potential for androgenetic alopecia in men and women.
By analyzing individual differences in genetic mutations, it may become possible to predict the responsiveness to each drug and the possibility of improvement of hair loss by medical treatment.
Genetic analysis may provide us with customized and effective treatments for hair loss in the near future.











