IGF-1

Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) is produced by dermal papilla cells.
IGF-1 increases hair growth, and it prevents the entry of hair follicles into the catagen phase.
Growth hormone and IGF-1 decrease testosterone and DHT in the area of AGA.
IGF-1 binds to IGF-1 Receptor
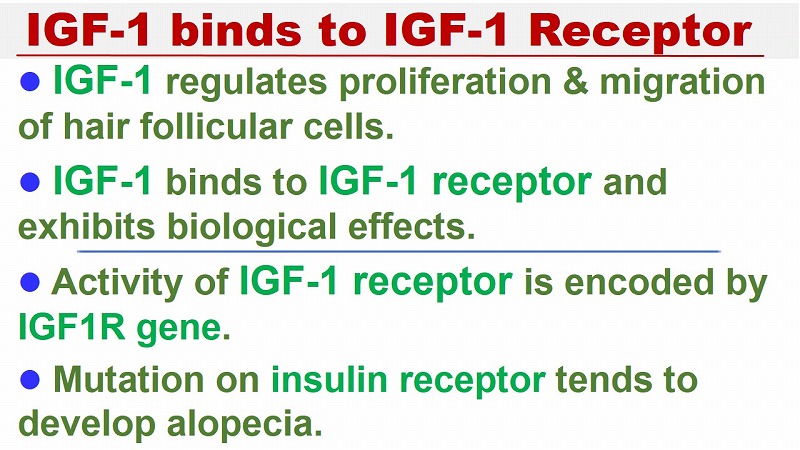
IGF-1 binds to receptors on the cell surface (IGF-1R) and regulates the migration and proliferation of hair follicular cells.
It has been reported that about 40% of people have low plasma IGF-1 levels, which may be due to allele mutations in the IGF-1R gene.
Recent studies have reported that insulin resistance and hyperglycemia increase serum IGF-1 levels, induce cell proliferation, and increase the risk of cancers in the liver, kidney, pancreas, colon and stomach in patients with type II diabetes.
IGF-1 also increases active estrogen which may result in an increased risk of breast cancer and uterus cancer in women.
High blood sugar, insulin resistance and IGF-1 can also cause mitochondrial dysfunction, increase oxidative stress, impair DNA repair, and stimulate oncogenes.
Prostaglandin Metabolism

Prostaglandins (PG) are hormone-like substances made in the tissues.
There are many types of PGs that control blood pressure, body temperature, activation of inflammatory responses, contraction of smooth muscles, etc.











