5α-Reductase Inhibitors
Finasteride and Dutasteride
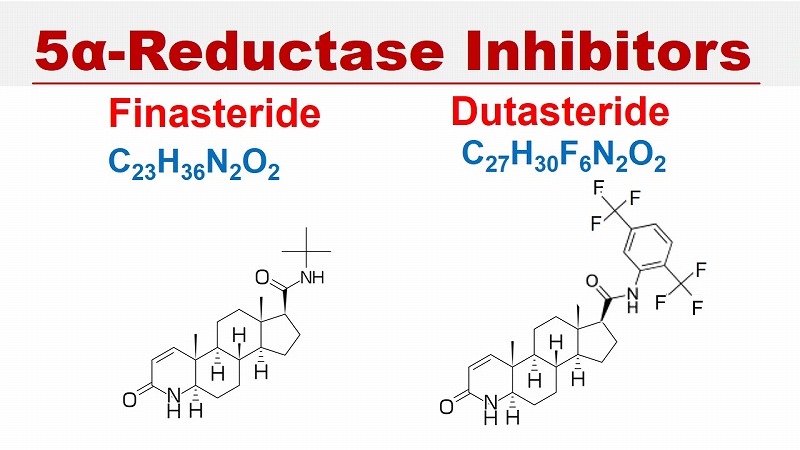
Finasteride and dutasteride do not completely block 5α-reductase.
With respect to the tissue DHT, finasteride and dutasteride have been reported in the literature to reduce tissue DHT levels by 60-70% and 90-97% respectively in men with AGA or prostatic cancer.
As for the serum DHT levels, both finasteride and dutasteride decreased serum DHT levels by about 50-60% in men with AGA (unpublished personal data).
There were individual differences, however, in the degree of serum DHT lowering effects between the drugs.
Generic drugs do not always work in the same way as brand-name drugs.
The brand-name finasteride had sometimes a better decrease in the serum DHT levels than generic finasteride in certain patients.
However, generic finasteride had sometimes a better decrease in the serum DHT levels than the brand-name finasteride in other patients according to the author’s personal experiences.
Dutasteride sometimes decreased the serum DHT better than finasteride in some specific patients.
However, there were other patients, in whom dutasteride did not reduce serum DHT, and finasteride reduced serum DHT better than dutasteride (unpublished data from the author).
The differences in the serum DHT lowering effects can come from the differences in the genes in each patient.
Analysis of genetic mutations may provide us with information about the effectiveness of different 5α-reductase inhibitors in each patient.
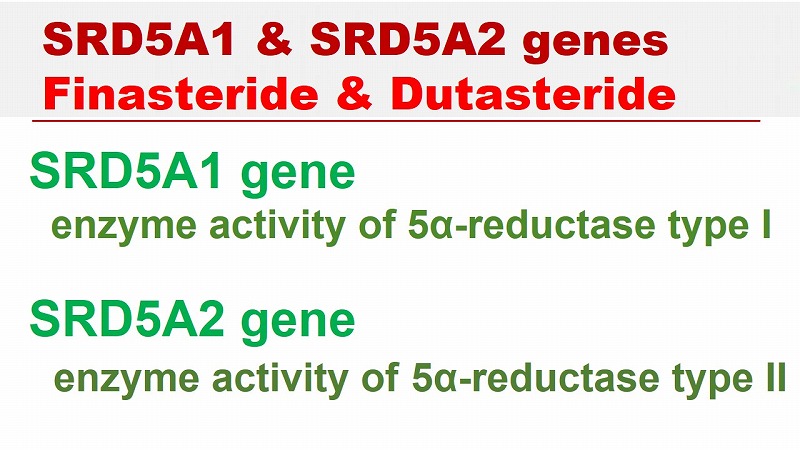
SRD5A1 and SRD5A2 genes;
Finasteride and Dutasteride
Finasteride inhibits 5alpha-reductase (5α-reductase) type II. Dutasteride inhibits 5α-reductase type I and II.
The steroid 5α-reductase (SRD5A) gene is associated with the activity of 5α-reductase type I and type II isoenzymes.
The SRD5A1 is a gene encoding the human 5α-reductase type I isoenzyme, while type II 5α-reductase isoenzyme is encoded by the SRD5A2 gene. There are three forms of steroid 5α-reductase, and these are two of them.
The C allele of the SRD5A1 gene has been reported to be found in about 40% of the population, resulting in high activity of 5α-reductase type I and high DHT levels.
SRD5A2 Gene
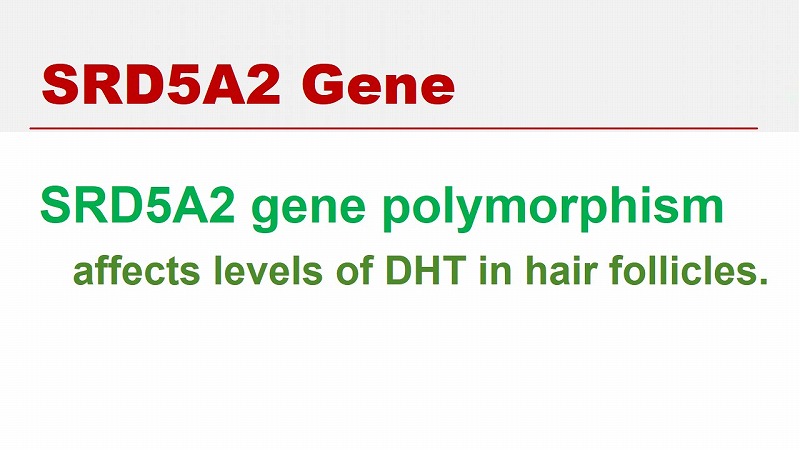
Steroid 5 alpha-reductase (5α-reductase) type 2 (SRD5A2) modifies testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the prostate and hair follicles.
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the SRD5A2 gene affected the levels of DHT in the hair follicles.
The G allele of the SRD5A2 gene is reported to be found in about 30% of the population, which was associated with the most active form of the enzyme, while the presence of the C allele made the enzyme less active.











